Heartwarming Info About How To Check For Dvt
Learn how deep vein thrombosis is diagnosed, from a medical history and physician exam to duplex ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (mri).
How to check for dvt. Your provider may use a ct scan to find a dvt in your abdomen, pelvis or brain, as well as blood clots in your lung (pulmonary embolism). Sudden coughing, which may bring up blood. The tests you have depend on whether.
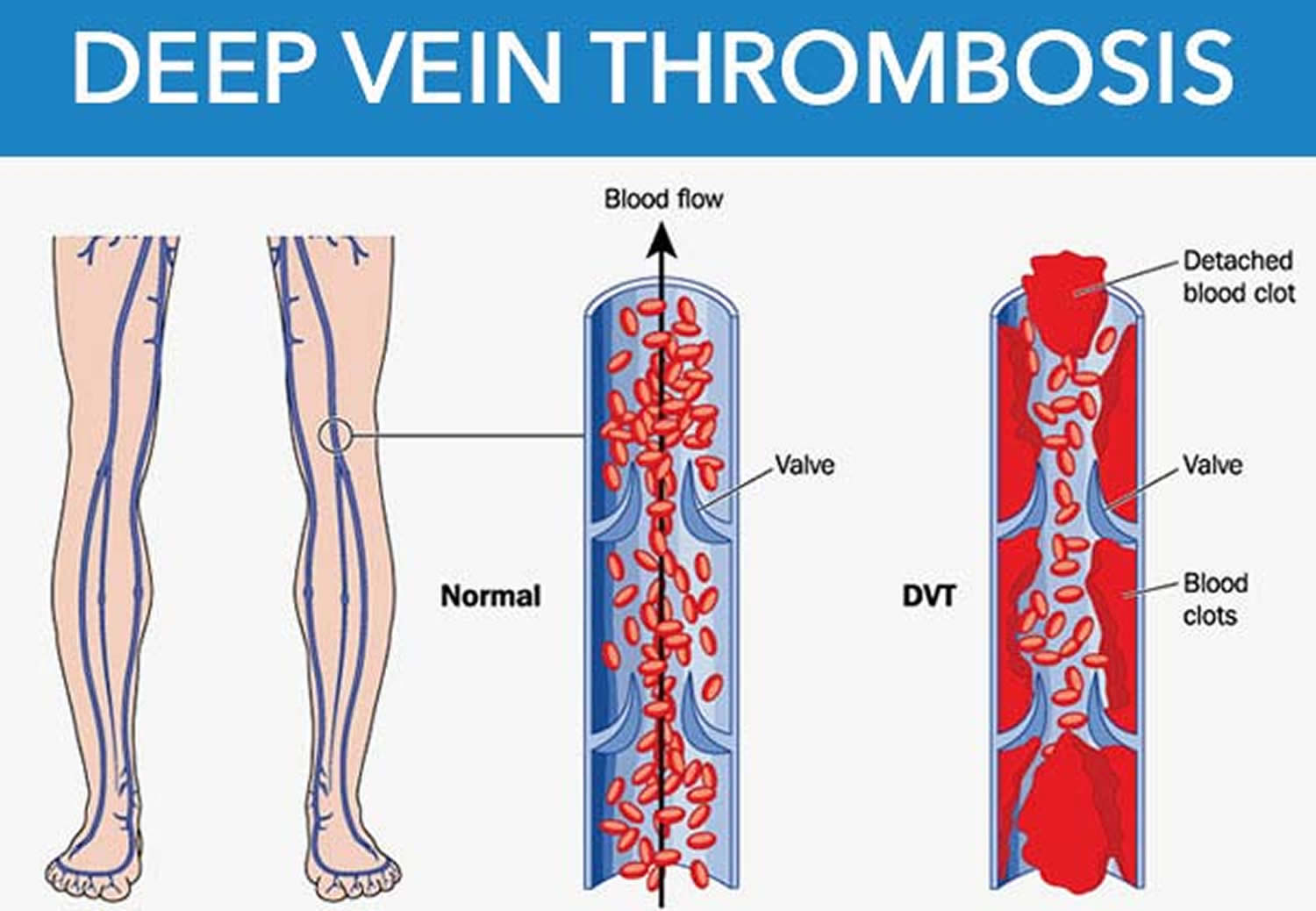
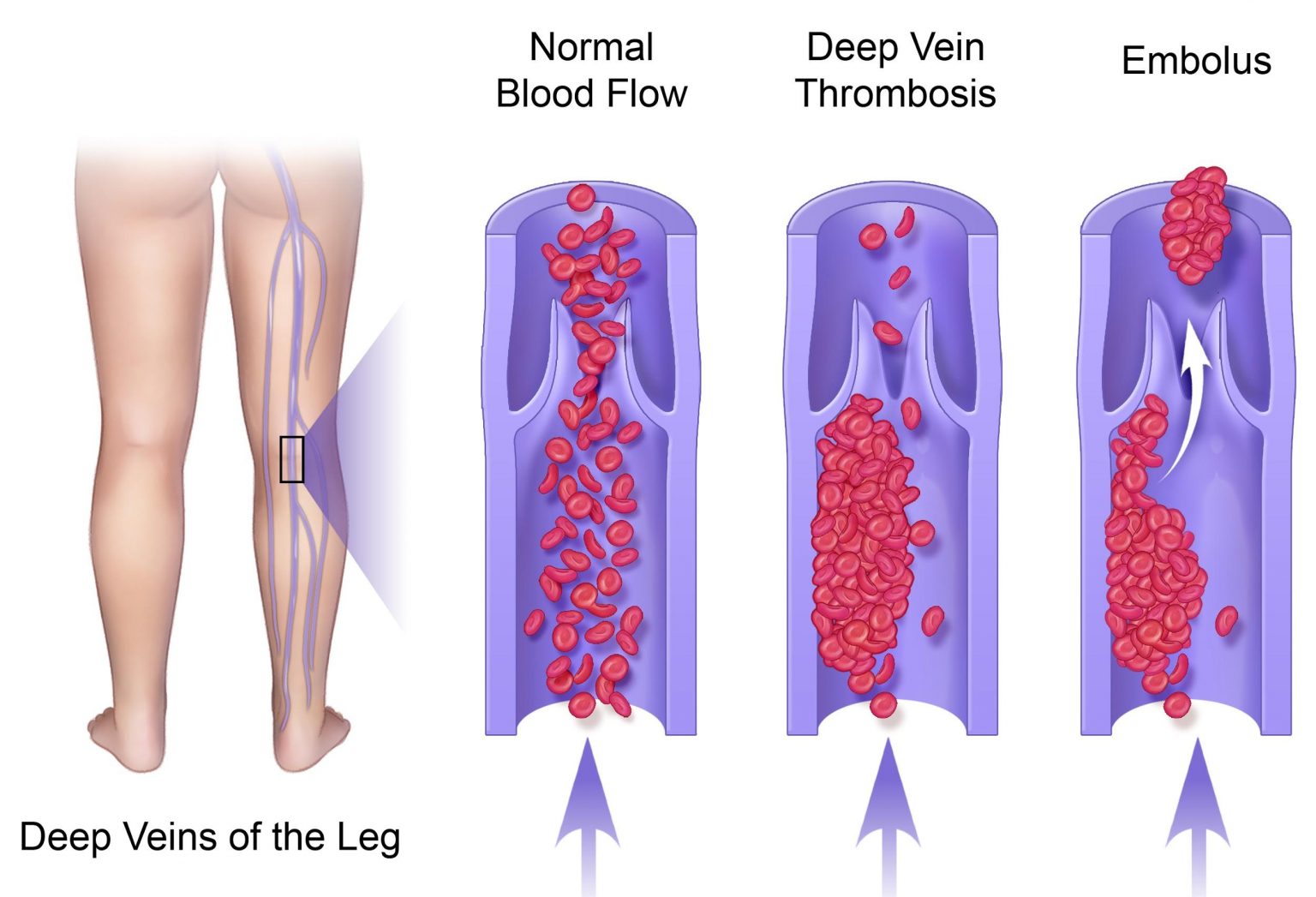
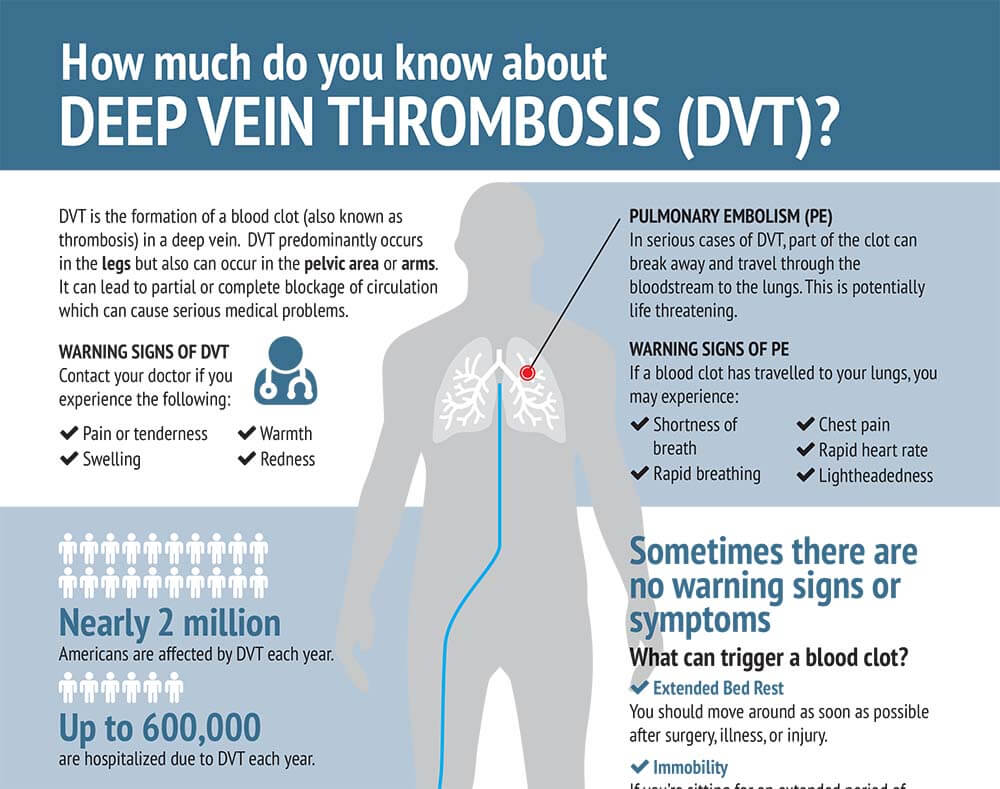
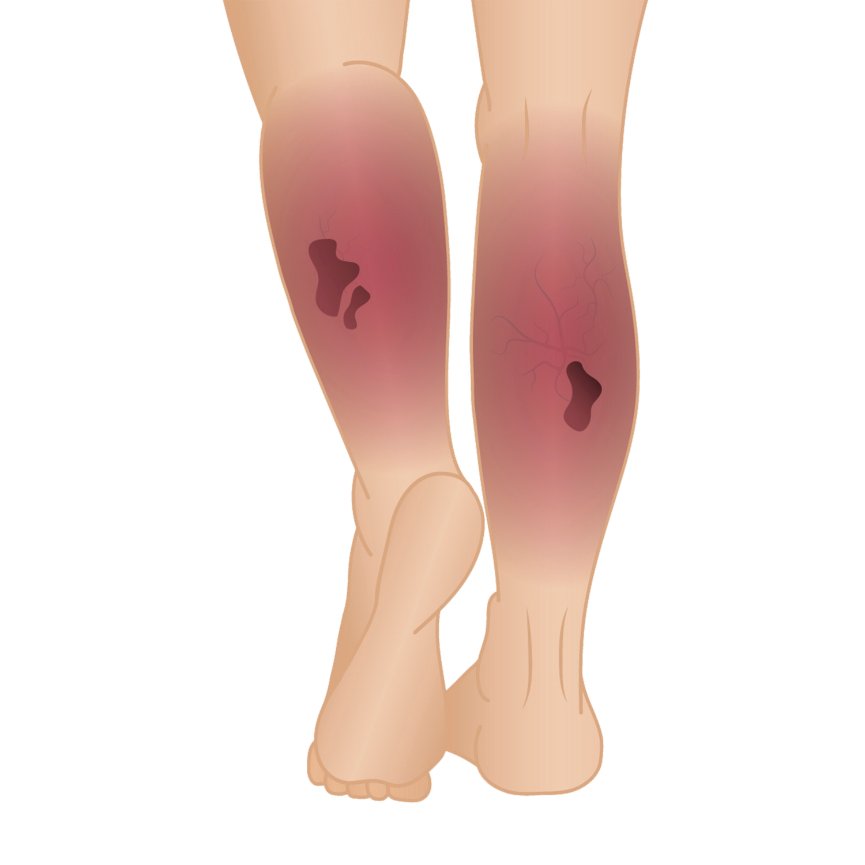
A deep vein thrombosis (dvt) is a blood clot in a vein. Swelling in the arm or hand. Learn how to check for dvt (deep vein thrombosis) at home with a simple test and some symptoms to look out for.
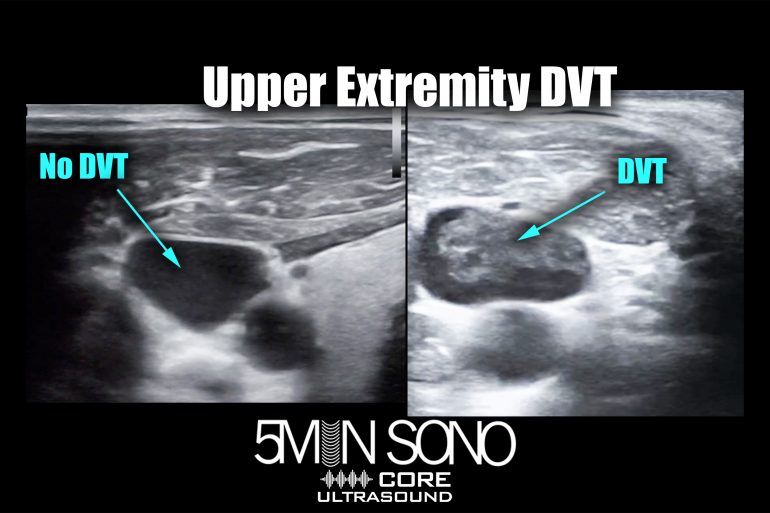
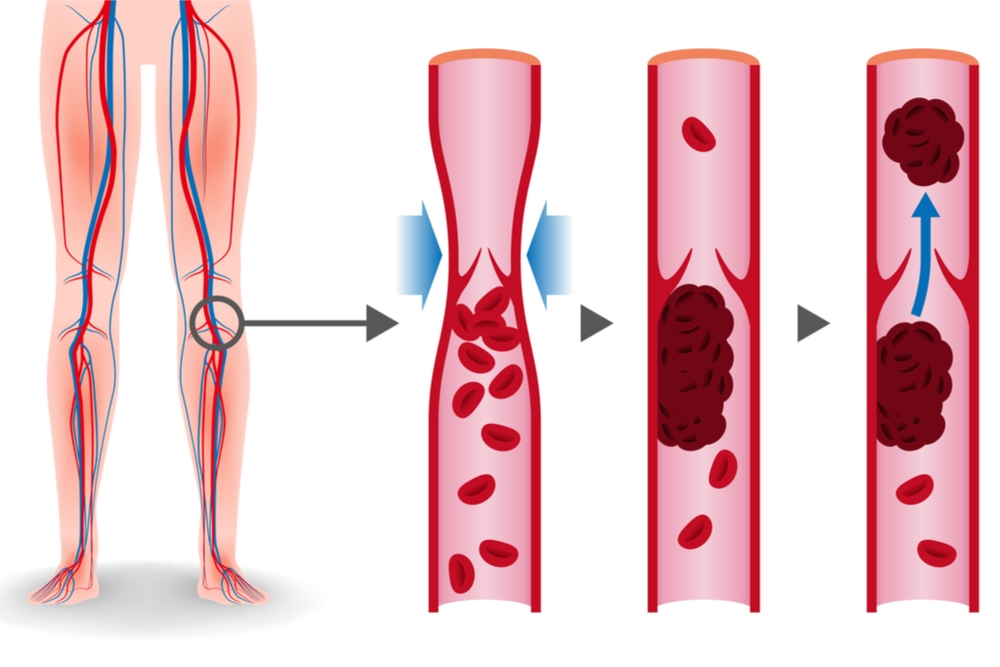
Scan the common femoral vein. Interpretation of the wells score for dvt. Anything that slows blood flow in deep veins can.
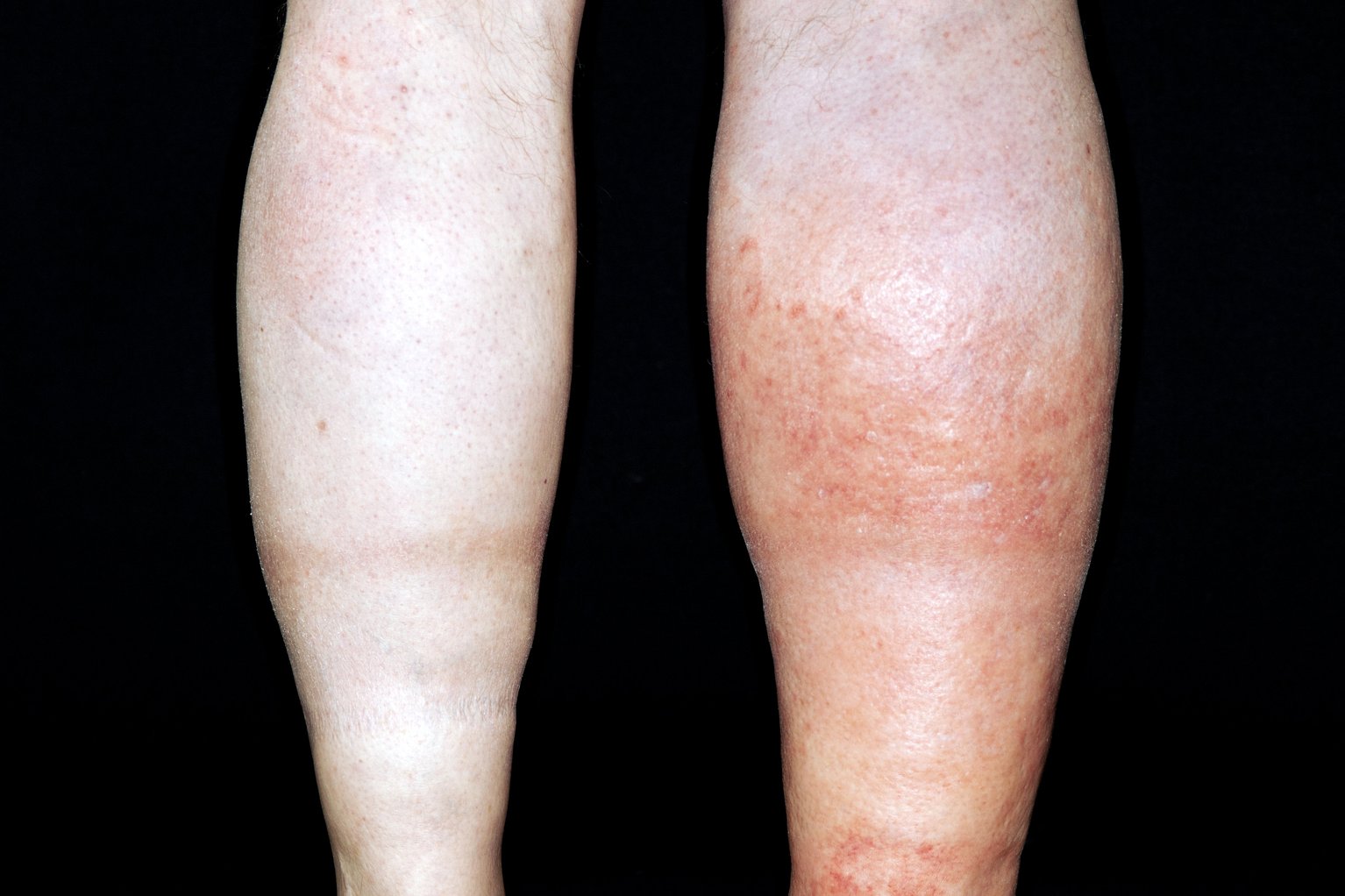
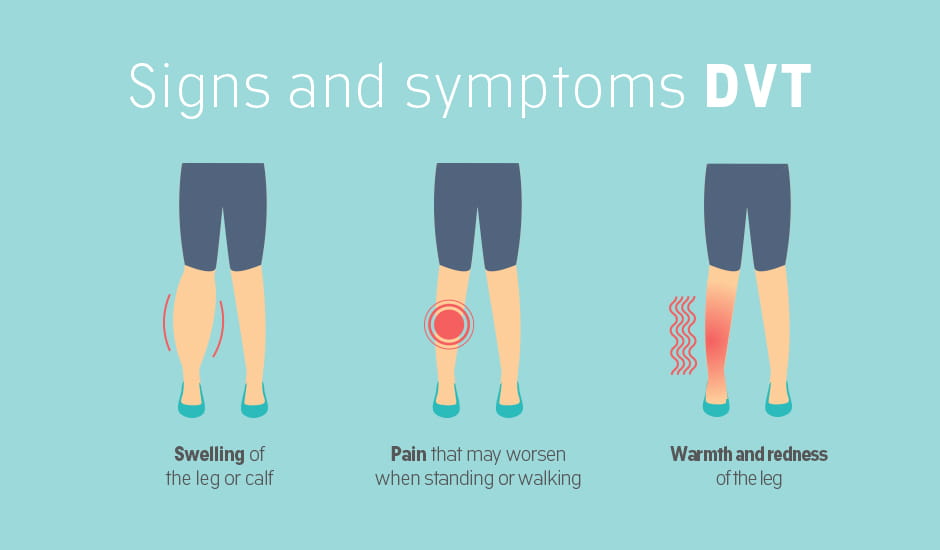
Find out why you should not treat dvt at home. To diagnose deep vein thrombosis (dvt), your health care provider will do a physical exam and ask questions about your symptoms. Call 911 or go to an emergency room right away if you notice leg pain or swelling and:
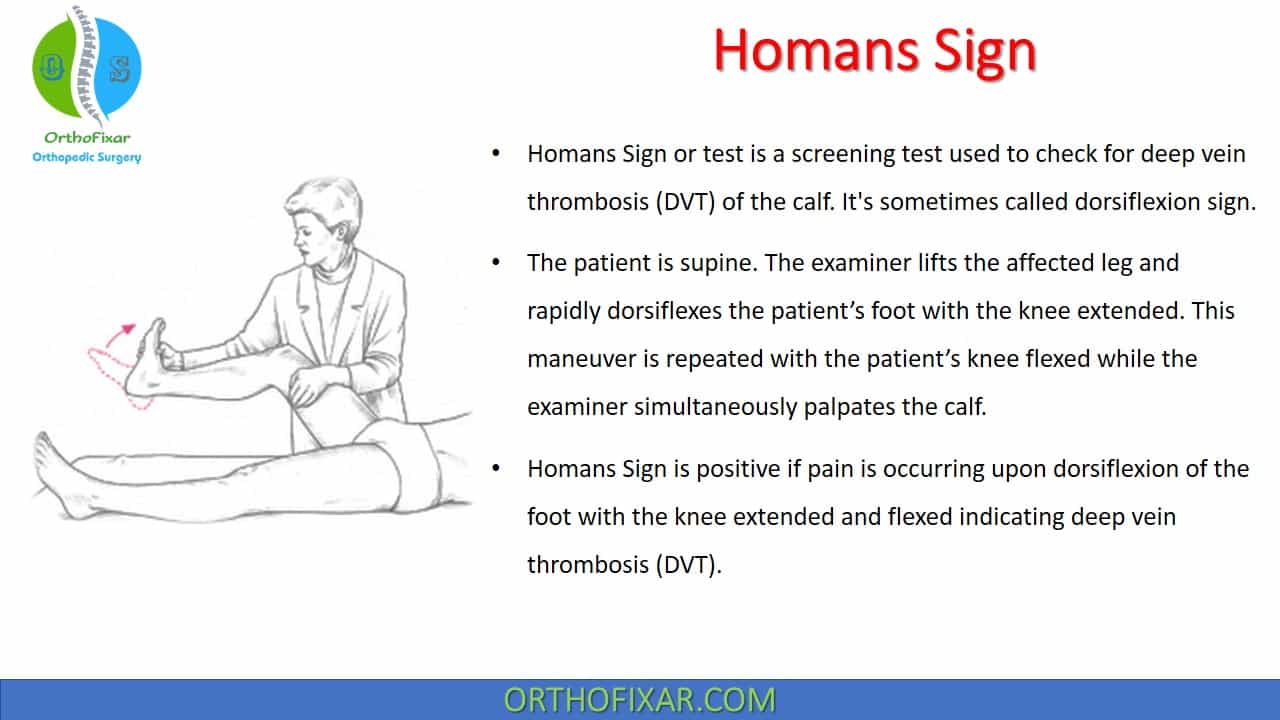
The provider will check the legs for swelling, tenderness or changes in skin color. Tests at your doctor’s office. Scan the (superficial) femoral vein.
People may not find out they have. Dvt likely (≥2 points) if a dvt is likely, a. Check your symptoms — use the symptom checker and find out if you need to seek medical help.
When a blood clot forms in one of the deep veins in your arm or leg, way beneath your skin's surface, it could be something called a deep vein thrombosis (dvt). If your doctor thinks you. It's what a blood clot makes as it dissolves inside your body.
Pain that moves from the arm to the forearm. How is dvt diagnosed? Sharp chest pain or chest tightness.
Your provider will diagnose dvt based on your symptoms, medical history, a physical exam, and various imaging or blood test results. The test can help providers pin down a diagnosis. Scan the great saphenous vein.